
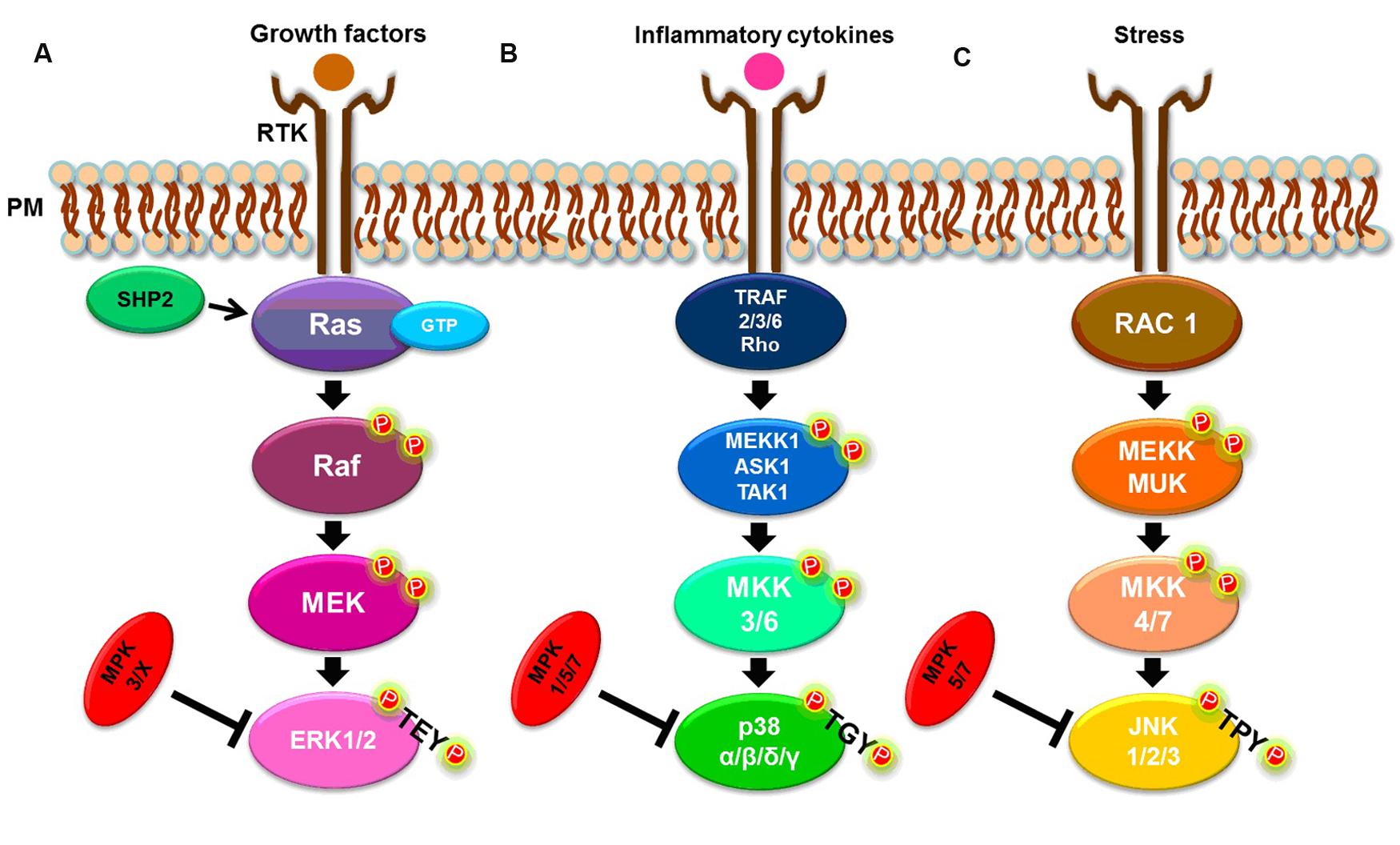
Received: JAccepted: DecemPublished: January 7, 2019Ĭopyright: © 2019 Ren et al. Copenhaver, The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, UNITED STATES (2019) BRASSINOSTEROID-SIGNALING KINASE 3, a plasma membrane-associated scaffold protein involved in early brassinosteroid signaling. Together, our findings elucidate the function of BSK3 in BR signaling and plant growth and development, and provide new insights into early BR signaling mechanisms.Ĭitation: Ren H, Willige BC, Jaillais Y, Geng S, Park MY, Gray WM, et al. BSK3 activates BR signaling via upregulating BSU1 transcript levels, and BIN2 phosphorylation of BSK3 influences BSK3 interactions with other signaling components, revealing new layers of regulation in BR signaling. BSK3 is important for BR-mediated root growth, shoot growth, and organ separation. Our genetic and biochemical studies suggest that BSK3 may function as a scaffold protein to regulate BR signaling. Here, we focus on BSK3 and investigate its function in BR signaling and plant growth and development. However, the functions of these receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases in the BR signaling pathway are poorly understood. Discovered in 2008, the BRASSINOSTEROID-SIGNALING KINASE (BSK) protein family is composed of twelve members. Brassinosteroids (BRs) are steroid hormones that regulate numerous growth and developmental processes throughout the plant life cycle. Steroid hormones exist in both animals and plants. The results of our studies provide new insights into early BR signaling mechanisms. Together, our findings suggest that BSK3 may function as a scaffold protein to regulate BR signaling. BSK3 is broadly expressed and plays an important role in BR-mediated root growth, shoot growth, and organ separation. Furthermore, we find that BSK3 upregulates BSU1 transcript and protein levels to activate BR signaling. BIN2 phosphorylation of BSK3 enhances BSK3/BSK3 homodimer and BSK3/BSK1 heterodimer formation, BSK3/BRI1 interaction, and BSK3/BSU1 interaction. BSK3 directly interacts with the BSK family proteins (BSK3 and BSK1), BRI1 receptor kinase, BSU1 phosphatase, and BIN2 kinase. Our genetic studies indicate that kinase dead BSK3 K86R protein partially rescues the bsk3-1 mutant phenotypes.
Interestingly, the effects of BSK3 on BR responses are dose-dependent, depending on its protein levels.
The N-terminal kinase domain is crucial for BSK3 function, and the C-terminal three tandem TPR motifs contribute to BSK3/BSK3 homodimer and BSK3/BSK1 heterodimer formation. We find that BSK3 is anchored to the plasma membrane via N-myristoylation, which is required for its function in BR signaling. We therefore investigated the function of BSK3, a receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase, in BR signaling and plant growth and development. Through forward genetics, we identified five semi-dominant mutations in the BSK3 gene causing BSK3 loss-of-function and decreased BR responses. The BR signaling pathway has been studied in some detail, however, the functions of the BRASSINOSTEROID-SIGNALING KINASE (BSK) family proteins in the pathway have remained elusive. Brassinosteroids (BRs) are steroid hormones essential for plant growth and development.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
